Chinese launch startup Space Circling, known officially as Shaanxi Tianhui Aerospace Technology Co., Ltd., has successfully clinched over 100 million yuan ($13.9 million) in funding to bolster its pioneering work on innovative rocket engines aimed at powering commercial space endeavors.
The Series A funding, unveiled on February 18th, marks a significant milestone for the Xi’an-based company, which secured the financing in December last year. Among the strategic investors contributing to the round are Changsha Kaifu District Zhongxin High-tech Fund, Mianyang Kefa Fund, Xi’an Fulao Fund, SIRI New Materials, and Xi’an Talent Fund, with the latter being a local government-backed policy guidance fund. Such funds are instrumental in channeling capital toward strategic and nascent technologies, including those in the space domain.
The injection of funds will primarily fuel the establishment of an industrial base dedicated to the production of rocket engines by Space Circling. Notably, the company has been engaged in the development of its Honglong-1 and Qiaolong-1 kerosene-liquid oxygen rocket engines since its inception in March 2021.
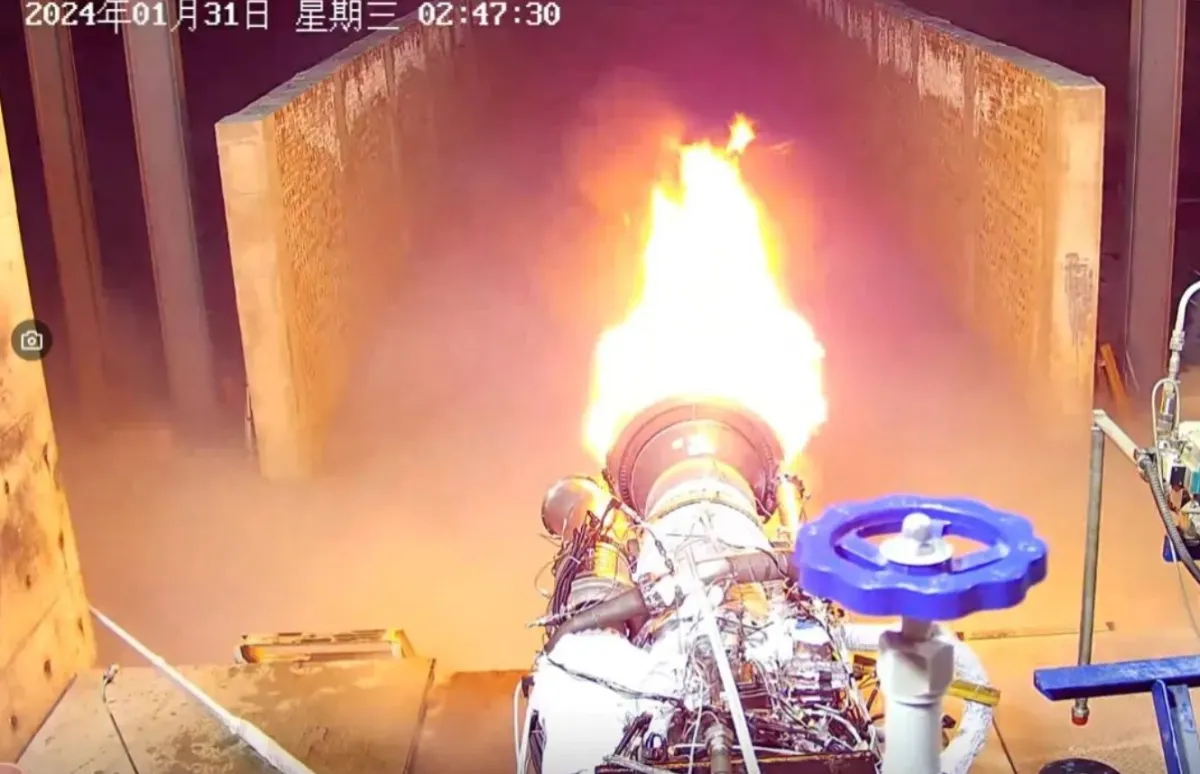
The Qiaolong-1, characterized by a staged combustion, tap-off cycle featuring two combustion chambers, represents a significant advancement in propulsion technology. Designed to generate 85 tons of thrust at sea level, the engine boasts a compact form factor, enabling the accommodation of five engines within a 3.35-meter-diameter stage—aligning with the standard sizing prevalent among Chinese Long March and commercial launch vehicles. Notably, Space Circling recently conducted a successful hotfire test of the engine on January 31st.
Founder Liu Hongjun, a professor at Northwestern Polytechnical University in Shaanxi, expressed ambitious aims for Space Circling’s endeavors. “Our team aims to fundamentally reduce the cost of human access to space and promote the arrival of a new economic era in space,” Liu stated on Space Circling’s official webpages.
Furthermore, Space Circling is poised to venture into the realm of reusable launchers, leveraging its cutting-edge engines. The Huilong-1, with dimensions including a length of 38 meters, a 3.35-meter-diameter core stage, and 2.25-meter-diameter boosters, is anticipated to lift payloads of up to five metric tons to sun-synchronous orbit. Meanwhile, the larger Huilong-2 is projected to have the capability of carrying nine tons to geosynchronous transfer orbit or 25 tons to Low Earth Orbit (LEO).
The support garnered by Space Circling underscores a broader trend within China, where various cities and provinces are actively nurturing their commercial space and high-end technology sectors. With the backing of provincial initiatives aimed at fostering innovation and industry chains, Space Circling and similar ventures stand poised to propel China’s space capabilities to new heights, potentially enhancing its international standing and influence in the global space arena.
That’s how they delete the gas-generator to make the engine slim. https://t.co/hIeBD8Izhr pic.twitter.com/TS6G8v4QZD
— Ace of Razgriz (@raz_liu) January 31, 2024